Banana Wine Manufacturing - A Comprehensive Guide to Start Your Business

In recent years, the world of alcoholic beverages has witnessed a surge in interest toward unique and exotic concoctions. Among these, banana wine has emerged as a flavorful and distinctive option, captivating the palates of connoisseurs and casual drinkers alike. With its rich aroma, smooth texture, and delightful taste, banana wine presents a lucrative opportunity for aspiring entrepreneurs in the beverage industry. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of banana wine manufacturing, exploring its production process, market potential, and the steps to launch a successful banana wine business.
Bananas are tropical fruits known for their soft flesh and elongated, generally yellow peel.
Banana wine, also known as banana beer or mbege in East Africa, is an alcoholic beverage made from fermented bananas. Unlike traditional grape wine, which relies on grapes as its primary ingredient, banana wine offers a unique flavor profile characterized by the natural sweetness and aroma of ripe bananas. The production process involves fermenting mashed bananas with yeast, sugar, and water, resulting in a delicious and refreshing beverage with varying levels of alcohol content.
Banana Wine Production Process:
The production of banana wine involves several key steps, each crucial to achieving the desired flavor, aroma, and alcohol content:
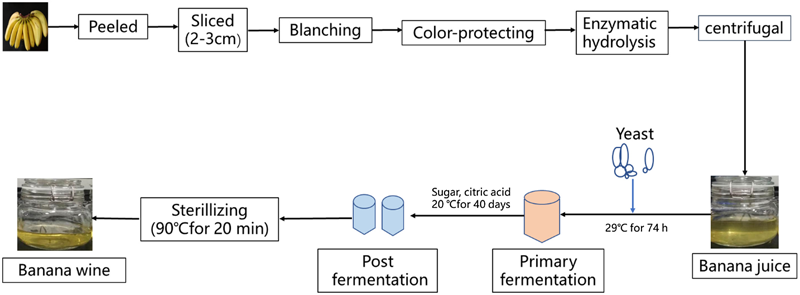
- Selection of Bananas: The first step in banana wine manufacturing is the careful selection of ripe and high-quality bananas. Varieties such as Cavendish, Gros Michel, or Lady Finger are commonly used for their sweetness and flavor.
- Preparation and Mashing: The selected bananas are peeled, mashed, and mixed with water to create a banana pulp. This pulp serves as the primary ingredient for fermentation.
- Addition of Ingredients: To initiate fermentation, sugar and yeast are added to the banana pulp mixture. The sugar provides food for the yeast, which converts the sugars in the bananas into alcohol and carbon dioxide.
- Fermentation: The banana pulp mixture is transferred to fermentation vessels, where it undergoes anaerobic fermentation. This process typically takes several days to weeks, during which the yeast converts the sugars into alcohol, resulting in the formation of banana wine.
- Clarification and Aging: After fermentation, the banana wine is clarified to remove any sediment or impurities. It may then be aged in oak barrels or stainless steel tanks to enhance its flavor and aroma.
- Bottling and Packaging: Once aged to perfection, the banana wine is bottled and packaged for distribution. Labels and branding play a crucial role in attracting consumers and establishing a distinctive brand identity.
Market Potential of Banana Wine:
The global banana market was worth USD 13,636.21 million in 2022 and is expected to reach USD 20,264.71 million by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 4.5% during 2023-2031.
The market potential for banana wine is significant, driven by several factors:
- Growing Consumer Interest: With an increasing demand for unique and artisanal beverages, banana wine appeals to consumers seeking novel flavor experiences beyond traditional options.
- Health Benefits: Bananas are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, making banana wine a healthier alternative to some other alcoholic beverages. The natural sweetness of bananas also reduces the need for added sugars, appealing to health-conscious consumers.
- Cultural Significance: In regions where bananas are abundant, such as tropical countries in Africa, Asia, and Latin America, banana wine holds cultural significance as a traditional beverage enjoyed during celebrations and special occasions.
- Versatility: Banana wine can be enjoyed on its own as a refreshing drink or used as a base for cocktails and culinary creations. Its versatility makes it a popular choice among mixologists and chefs looking to experiment with new flavors.
Market Trends, Drivers, Restraints, and Opportunities
Consumer preferences in the banana market are influenced by a growing emphasis on clean and healthy food products. As advancements in food and beverage technology continue and health awareness rises, consumers are increasingly seeking natural and nutritious options. Bananas, with their inherent nutritional benefits and natural properties, are gaining traction as a favored choice among health-conscious consumers.
Moreover, bananas are finding versatile applications across various food products, further driving market growth. From being used in smoothies and ice cream to desserts, pancakes, and breakfast cereals, bananas offer a versatile and flavorful addition to a wide range of culinary creations. This expanding utilization of bananas in diverse food items contributes significantly to the burgeoning demand in the global banana market.
However, the banana market is not without its challenges. Natural disasters such as hurricanes, floods, or diseases can disrupt banana production, particularly in organic cultivation. These disruptions in supply chains can lead to shortages and price fluctuations, impacting market dynamics and consumer access to bananas.
Additionally, distribution challenges and regulatory compliance pose significant hurdles for banana producers and distributors. Issues related to transportation logistics and adherence to strict food safety and quality standards can affect market operations and trade flows. Overcoming these challenges requires robust supply chain management and compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Consumer Preference for Clean and Healthy Food Products: With advancements in food and beverage technology and increasing health awareness among consumers, there is a noticeable shift towards clean and healthy food choices. This trend influences the demand for bananas, known for their nutritional value and natural properties.
- Growing Use of Bananas in Various Food Products: Bananas are versatile fruits used in a wide range of food products such as smoothies, ice cream, desserts, pancakes, and breakfast cereals. The increasing utilization of bananas in these food items contributes to the growth of the global banana market.
- Impact of Natural Disasters: Natural disasters such as hurricanes, floods, or diseases can adversely affect banana production, particularly organic cultivation. These disruptions in production can lead to supply shortages, impacting the banana market and causing fluctuations in prices.
- Distribution Challenges and Regulatory Compliance: Distribution issues, including transportation logistics and regulatory compliance, pose challenges for the banana market. Strict regulations related to food safety and quality standards must be adhered to, which can affect market dynamics and trade.
- Opportunities in Manufacturing Clusters: Identifying manufacturing clusters for industrially processed banana products presents opportunities for new businesses. By focusing on areas with existing infrastructure and expertise, companies can capitalize on the growing demand for processed banana products and expand their market presence.
Amidst these challenges, opportunities abound in identifying and capitalizing on manufacturing clusters for industrially processed banana products. By focusing on regions with established infrastructure and expertise in banana processing, new businesses can tap into the growing demand for processed banana items. This strategic approach allows companies to expand their market presence and cater to evolving consumer preferences for banana-based products.
Banana wine manufacturing offers a unique opportunity for entrepreneurs to tap into the growing demand for artisanal and exotic beverages. With its distinct flavor, cultural significance, and health benefits, banana wine has the potential to carve out a niche in the competitive alcoholic beverage market. By understanding the production process, market potential, and key steps to launch a successful business, entrepreneurs can embark on a rewarding journey into the world of banana wine manufacturing. Cheers to sweet success!










