Future of Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Manufacturing and Assembly
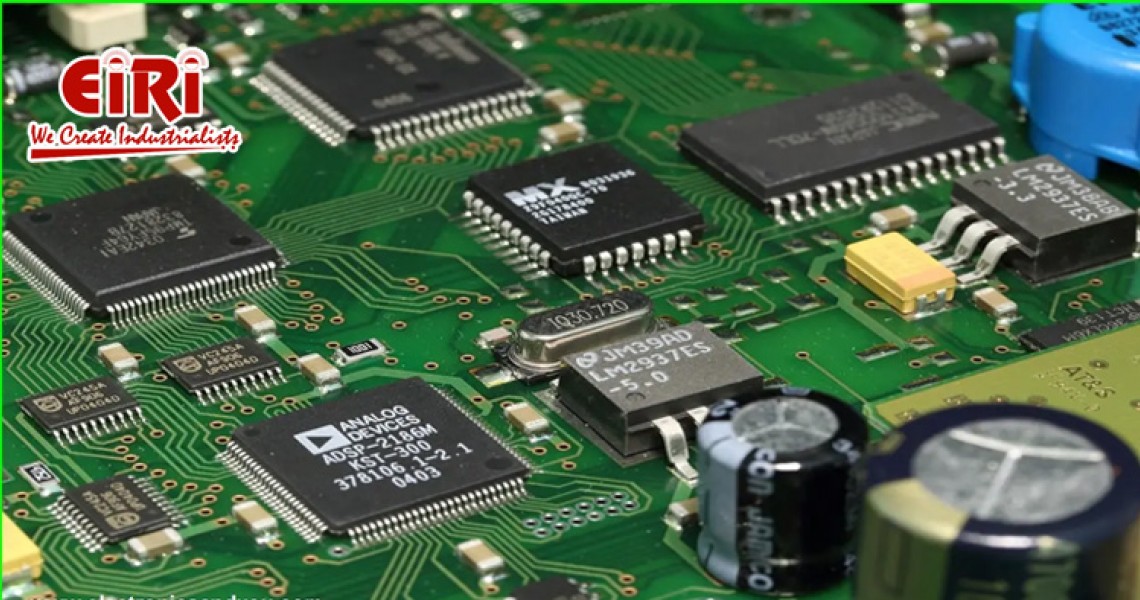
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are foundational components in electronic devices, serving as the mechanical support and electrical connection platform for various electronic components. They are flat, rigid boards made of non-conductive materials like fiberglass or composite epoxy laminate, with thin layers of conductive material (usually copper) etched or printed onto the surface.
PCBs facilitate the assembly and interconnection of electronic components by providing conductive pathways or "traces" that carry electrical signals between different parts of the circuit. These traces are typically created using a process called etching, where unwanted copper is removed from the board, leaving behind the desired pattern of conductive pathways.
PCBs come in various types, including single-layer, double-layer, and multi-layer boards, depending on the complexity of the circuitry and the number of layers of conductive material used. They are essential in modern electronics, used in everything from smartphones and computers to medical devices and automotive systems.
Overall, PCBs play a crucial role in enabling the functionality of electronic devices by providing a reliable and compact platform for connecting and integrating electronic components.
PCB Industry Market Dynamics
The dynamics of the Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) market are driven by several factors shaping its growth trajectory in the global electronics industry. With the increasing demand for multifunctional systems and high-tech smart devices, PCBs have emerged as crucial components determining both the functionality and aesthetics of electronic equipment. This rising demand for electronic gadgets such as smartphones, computers, and telecommunication devices is fueling the growth of the global PCB market. Additionally, PCBs play a vital role in industrial equipment, including cell towers, automated machinery, and other machines, facilitating rapid operation and process improvement.
Projected for 2032, the PCBs market, valued at $11.72 billion in 2022, is estimated to reach $14.72 billion, with a 3.3% CAGR from 2023-2032.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the demand for electronic devices as remote work and online learning became the new normal. This surge in demand for smartphones, computers, tablets, and medical equipment has directly contributed to the growth of the PCB industry. However, alongside this growth, stringent regulations governing e-waste generated from PCBs have emerged as a significant challenge. Hazardous compounds used in PCB manufacturing, such as lead, epoxy resins, cadmium, and mercury, pose environmental concerns and require proper disposal measures. These regulations have compelled PCB manufacturers to adhere to stricter standards, impacting their profitability.
PCBs find extensive use across various industries, including the industrial, medical, and automotive sectors. In the industrial sector, PCBs are essential for day-to-day operations and automation, helping organizations save costs and minimize human error. They can be customized to handle high-power applications and harsh environmental conditions prevalent in manufacturing facilities. Similarly, in the medical industry, PCBs are integral to appliances, monitoring devices, diagnostic equipment, and therapy tools. The use of PCBs in the medical field is expanding rapidly with advancements in technology, enabling innovative solutions for healthcare providers.
Moreover, the automotive sector has witnessed a significant integration of PCBs and electronic components in modern vehicles. From navigation systems to advanced car control systems, PCBs play a crucial role in enhancing the functionality and safety features of automobiles. Navigation technologies such as satellite navigation and advanced driver assistance systems rely on PCBs for their operation. Additionally, PCBs are utilized in monitoring and regulating various vehicle components, including power supply, fuel regulators, and engine management systems.
PCB Current Market Trend
The current trends and market dynamics in the Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) industry are shaped by the evolving needs of consumers and advancements in technology. In the early 2020s, there is a notable shift towards smaller and more flexible computing options, driving PCB manufacturers to adapt and innovate to meet these demands.
One significant trend in the PCB market is the widespread adoption of High-Density Interconnect (HDI) technology. HDI has emerged in response to the increasing demand for faster and more compact interconnectivity between devices. With HDI, manufacturers can produce smaller wireless products with enhanced routing capability and faster signal transmission. This technology has enabled the development of units with simpler PCB stackup, complemented by anti-interference technologies such as every layer interconnect (ELIC) and any layer interconnect (ALIC).
Another prominent trend is the development of High-Power Boards to meet the growing energy and processing requirements of advanced computer technology. These high-powered PCBs, operating at 48V and higher, are essential for devices such as solar panels and battery packs. They offer increased resistance to interference and are crucial for powering modern computing devices.
The Internet of Things (IoT) continues to drive innovation in the PCB industry, with a focus on integrating everyday devices into a network controlled by wireless technology. IoT technology has found applications in smart homes, offices, and is poised to expand into smart automobiles. To address the challenges posed by IoT, PCB manufacturers are enhancing security standards to ensure the integrity and reliability of connected devices.
Flex PCBs have emerged as a novel development in printed circuit technology, offering flexibility and versatility in design. These PCBs can be bent and curled into various shapes, catering to the demand for smaller and more compact wireless devices. Flex PCBs enable device makers to manufacture products with unique form factors and improved portability.
Furthermore, there is a growing trend towards the use of Commercial-Off-The-Shelf (COTS) components as organizations seek more generalized technological solutions. This shift is driven by the need for standardized options and features, particularly in unconventional environments. Additionally, advancements in space manufacturing have contributed to the increased adoption of COTS components.
The Printed Circuit Board Assembly Market, valued at USD 9 billion in 2023, is expected to grow at a 10% CAGR from 2024 to 2032.
Lastly, there is a heightened focus on component supply chain control to ensure the security and authenticity of technological components. PCB manufacturers are leveraging augmented reality and virtual reality simulations during the assembly process to detect and eradicate counterfeit components. This emphasis on security aims to enhance the reliability and performance of computing frameworks, particularly as organizations operate remotely across vast distances.
The future of Printed Circuit Board
The impending decade will witness an era dominated by smart technology infiltrating various sectors, driving PCB manufacturers to innovate tailored solutions. Key trends encompass high-density PCBs for compact and versatile applications, enhanced cameras, 3D printing for prototyping, and smart office and factory setups facilitated by IoT-enabled PCBs. Moreover, the demand for high-speed PCBs to maintain signal integrity and adaptability to smaller devices via flexible PCBs are on the rise. Lastly, the emergence of biodegradable PCBs addresses environmental concerns, marking a shift towards sustainability in the industry.
1. High-Density PCBs:
- High-density circuit boards (HDI PCBs) are anticipated to see increased use in the coming years due to the demand for smaller and more complex devices.
- These boards offer advantages such as lighter weight, compact size, enhanced routing capability, and faster signal transmission.
- They allow for simpler stackup, improved electrical performance, cost-effectiveness, and quicker production time compared to traditional PCBs.
2. Enhanced Cameras:
- PCBs are being adapted to accommodate advanced features in commercial and industrial cameras.
- These advancements include higher mega-pixel specs, improved resolution, enhanced zoom capabilities, and freeze-frame clarity.
- Advanced filtering features are also being integrated to reduce the need for extensive photo editing, resulting in optimal imagery.
3. 3D Printing in PCB Manufacturing:
- 3D printing is finding applications in various industries such as apparel, automotive, food, and aerospace for prototype production and customization.
- PCBs with high-capacity components are essential for the functioning of 3D printers.
- There is potential for cloud-based manufacturing, allowing for remote design uploads and immediate printing capabilities.
4. Integration of IoT in Offices and Factories:
- The integration of IoT in office spaces and manufacturing facilities is increasing for automation and efficiency.
- This includes remote control of devices, centralized computing systems, and the implementation of smart functionalities.
- IoT capabilities are expected to boost efficiency in factories, with centralized control of machinery and equipment.
5. High-Speed PCBs:
- There is a growing need for PCBs capable of maintaining signal integrity in high-speed environments.
- Component placement is crucial for optimizing signal transmission and addressing challenges like crosstalk and attenuation.
- Focus is placed on designing boards that can handle high-speed data transmission without signal degradation.
6. Flexibility for Smaller Devices:
- Flexible PCBs are gaining popularity to accommodate smaller designs and extreme operating conditions.
- These boards offer advantages such as lightweight, portability, and adaptability, making them suitable for compact and high-stress applications.
- They enable product makers to modify boards to conform to the needs of specific devices, allowing for greater design flexibility.
7. Biodegradable PCBs:
- There is a growing trend towards the development and adoption of PCBs made from natural fibers to address environmental concerns.
- These biodegradable PCBs offer benefits such as the reduction of tech waste and eco-friendliness.
- There is potential for widespread adoption of biodegradable PCBs in the industry as companies aim to reduce their carbon footprint.
The PCB market dynamics are influenced by factors such as increasing demand for electronic gadgets, stringent regulations on e-waste management, and the widespread adoption of PCBs across industrial, medical, and automotive sectors. Despite challenges, the PCB industry continues to evolve and innovate, driven by advancements in technology and the growing need for reliable and efficient electronic solutions in diverse applications.










